The problem of foam in concrete has always been one of the key factors affecting the quality of engineering. This paper will start from the cause of formation of foam, deeply analyze its impact on concrete performance, and propose corresponding countermeasures.
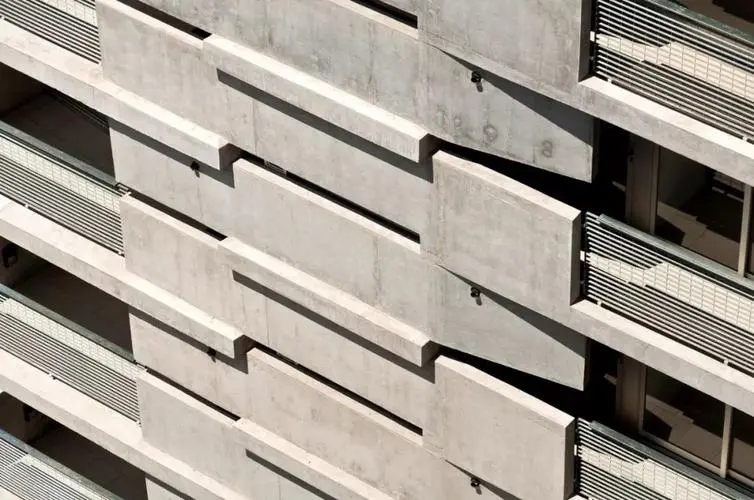

During the mixing process, air is carried into the concrete. Additives (such as water reducing agents, air entraining agents, etc.) react with cement to produce gas. Improper control of moisture content in raw materials leads to the introduction of excessive moisture that evaporates and forms bubbles.
Foam will reduce the compactness of concrete and affect the strength, impermeability and durability. In severe cases, it can also cause defects such as pitting and honeycombing on the surface of concrete, affecting its appearance and functionality.
For these foam problems, we should optimize the mixing process to reduce the air entrainment in the mixing process. Reasonably select additives, control their dosage and addition time. Strengthen the management of moisture content in raw materials to ensure the uniformity of concrete mixtures. Use appropriate defoamer to effectively
control and eliminate foam.

 English
English
 Chinese
Chinese Vietnamese
Vietnamese
 HOME
HOME
 PRODUCT
PRODUCT
 NEWS
NEWS
 CONTACT
CONTACT


