The mechanism of action and precautions of leveling agents
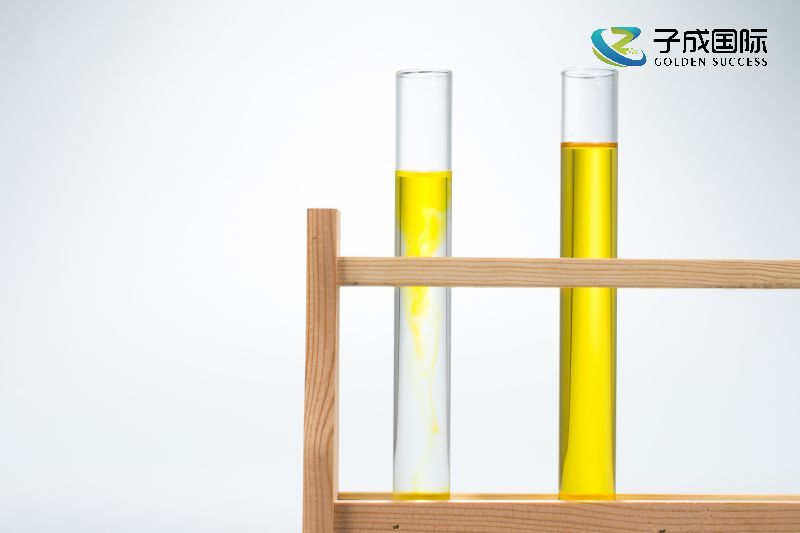

Reducing surface tension, leveling agents can lower the surface tension of coatings, making them easier to flow and spread during the coating process. This helps to reduce the uneven distribution and accumulation of coatings during the coating process, and improve the flatness and uniformity of the coating.
Improving fluidity, leveling agents interact with particles in the coating to reduce the friction between the coating particles and the surface, allowing for better flow and expansion. This helps to improve the flowability of the coating, making it easier to operate and control during the construction process.
Eliminating surface defects, leveling agents can reduce surface defects such as shrinkage and fish eyes that occur during the drying process of coatings. These defects often affect the appearance quality and durability of the coating. The addition of leveling agents can effectively eliminate these defects and improve the overall performance of the coating.
It is worth noting that we need to choose a suitable leveling agent. When selecting a leveling agent, it is necessary to comprehensively consider factors such as the type of coating, construction conditions, and usage requirements. Different types of coatings require different performance leveling agents to achieve the best leveling effect. Control the amount of addition, the amount of leveling agent added needs to be strictly controlled. Insufficient addition may not achieve the desired leveling effect; Excessive addition may lead to other adverse phenomena in the coating, such as sagging and poor drying.
Construction conditions: During the construction process, it is necessary to maintain the dryness and cleanliness of the coating and substrate surfaces to avoid the influence of impurities such as oil stains and dust on the coating quality. At the same time, it is necessary to control the temperature and humidity conditions of the construction environment to ensure the normal drying and curing of the coating.

 English
English
 Chinese
Chinese Vietnamese
Vietnamese
 HOME
HOME
 PRODUCT
PRODUCT
 NEWS
NEWS
 CONTACT
CONTACT


